ARRITHMIA AND ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
24 October 2025, Friday
Arrhythmia and Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
1. What are arrhythmia and atrial fibrillation (AF)?
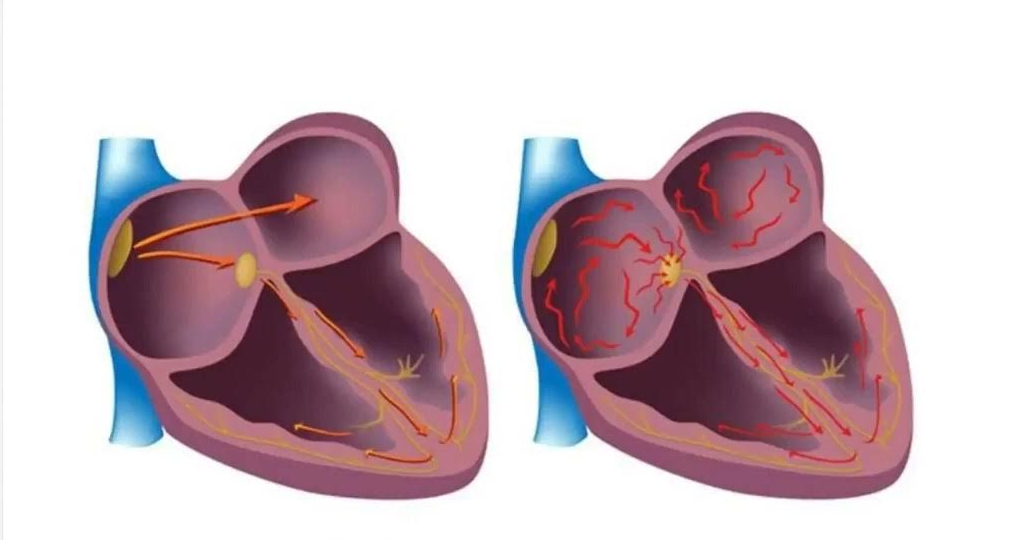
Arrhythmia is a disturbance of the normal heart rhythm that can manifest as acceleration, deceleration, or irregularity of heartbeats.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of sustained tachyarrhythmia, in which the atria contract chaotically and ineffectively. The ventricular rate may be normal, elevated, or decreased.
2. Causes
AF may be idiopathic (with no established cause), but is more often associated with structural heart disease or systemic conditions. The main causes include:
· Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Hypertension
- Heart failure
- Valvular heart disease (especially mitral)
- Cardiomyopathies
- Acute conditions: myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism
- Thyroid disorders (hyperthyroidism)
- Electrolyte disturbances
- Intoxications, including alcohol ("holiday heart syndrome")
3. Risk Factors
- Age > 65 years
- Arterial hypertension
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Chronic stress
- Increased physical or emotional stress
- Family history
4. Types and Classification of AF (per ESC, AHA/ACC)
- First diagnosed
- Paroxysmal — episode < 7 days, terminates spontaneously
- Persistent — episode > 7 days, requires pharmacologic/electrical intervention
- Long-standing persistent — lasts > 12 months
- Permanent — decision made not to restore rhythm, focus on rate control
·
5. Key Symptoms
- Palpitations, irregular heartbeats
- Rapid or irregular pulse
- Dyspnea on exertion
- Reduced exercise tolerance
- Fatigue, dizziness
- Syncope episodes
- Sometimes asymptomatic and detected incidentally
6. Diagnosis
- ECG (gold standard): absence of P waves, irregular rhythm
- 24-hour Holter ECG — for intermittent episodes
- Echocardiography (EchoCG) — to assess atrial size, LVEF, thrombi presence
- Blood tests:
- TSH, FT4 — to rule out thyrotoxicosis
- Electrolytes, creatinine
- Coagulation parameters (PT, INR — if on anticoagulants)
7. Current Treatment Approaches (ESC 2020, ACC/AHA 2019)
a) Rhythm control strategy:
- Pharmacologic cardioversion: propafenone, amiodarone
- Electrical cardioversion
- Catheter ablation (highly effective in paroxysmal AF)
b) Rate control strategy:
- Beta-blockers (metoprolol, bisoprolol)
- Non-dihydropyridine CCBs (verapamil, diltiazem)
- Digoxin (in heart failure patients)
c) Thromboembolism prevention:
Based on CHA₂DS₂-VASc score — if ≥1 in men and ≥2 in women:
- NOACs: rivaroxaban, apixaban, dabigatran
- Warfarin (if NOACs not available, INR monitoring required)
8. Possible Complications
- Ischemic stroke (up to 5x increased risk in AF)
- Heart failure
- Thromboembolism in other sites
- Decreased quality of life
- Tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy
- Cognitive impairment
9. Prevention
- Control of blood pressure and body weight
- Reducing alcohol and salt intake
- Treating obstructive sleep apnea
- Maintaining normal TSH levels
- Moderate physical activity
- Smoking cessation
10. When to See a Doctor
- If you feel irregular heartbeat or “skipped beats”
- In case of dyspnea, fatigue, dizziness
- If AF has already been diagnosed — for therapy selection and stroke risk evaluation
- For treatment monitoring (labs, Holter, therapy adjustment)
Cardiology Services at VitaMed Medical Center (Yerevan, Charentsavan, Stepanavan)
| Cardiologist home visit |
20.000 AMD |
| Electrocardiography |
4.000 AMD |
| Echocardiography |
15.000 AMD |
| ECG monitoring 24-hour (Holter monitoring) |
15.000 AMD |
| Daily blood pressure Monitoring (SMAD) |
8.000 AMD |
| Initial consultation with a cardiologist with the appointment of treatment, including an electrocardiogram |
15000 AMD |
| Initial consultation with a cardiologist without examination |
12000 AMD |
| Third visit to a cardiologist in a month |
5000 AMD |
Armen Shahbazyan, Cardiologist
Armen Shahbazyan, 11.01.1992 year of birth․
Education
- Yerevan State Medical University named after Mkhitar Heratsi, Faculty of General Medicine, Bachelor's degree 2008-2013.․
- Yerevan State Medical University named after Mkhitar Heratsi, Faculty of General Medicine, Master's Degree 2013-2015․
- Yerevan State Medical University named after Mkhitar Heratsi, Clinical residency in Cardiology, 2015-2018.
Professional activity
- "Aramyants" MC, 2018-2019, ITB as a cardiologist
- "Astghik MC" 2020-2022, ITB as a cardiologist
- "Nairi" MC, from 2019 to the present, cardiologist on duty
- "MedLine" MC, from 2022 to the present, cardiologist
- "VitaMed" MC, from 2022 to the present, cardiologist, a specialist in monitoring of Holter
Trainings
- Specialization "Echocardiography" in 2018․
- Specialization "Holter monitoring" in 2022․
 126
126


.jpeg)